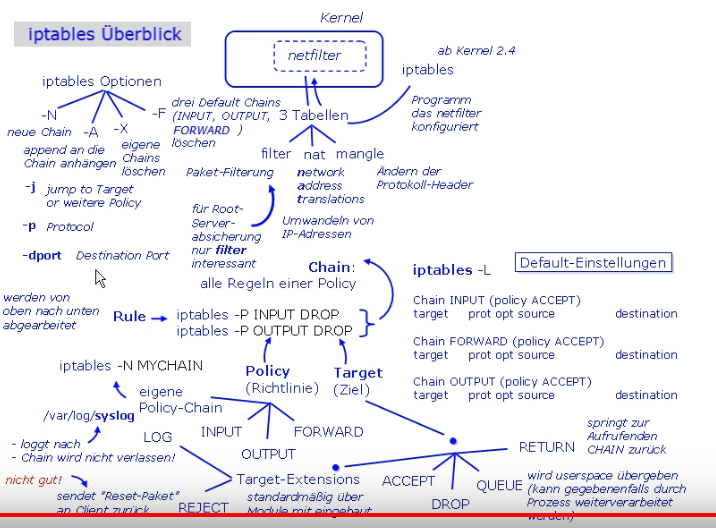
IPTables ist eine hauseigene Firewall für Linux ab Kernel 2.4. Genaugenommen ist es ein Tool das im Hintergrund Netfilter konfiguriert. Seit etwa Mitte 2018 wurde iptables durch nftables (netfilter tables) ersetzt, die Syntax blieb weitgehend gleich. ebtables ist wie IPTables aber für Layer 2 Frames.
Netfilter hat 3 Tabellen
- filter - Paketfilter
- nat - NAT
- mangle - Paketheader manipulieren
Targets
- return
- queue
- drop
- accept
- reject
- log - nach /var/log/syslog
Policies
- INPUT
- OUTPUT
- FORWARD
# statistics iptables -L -v
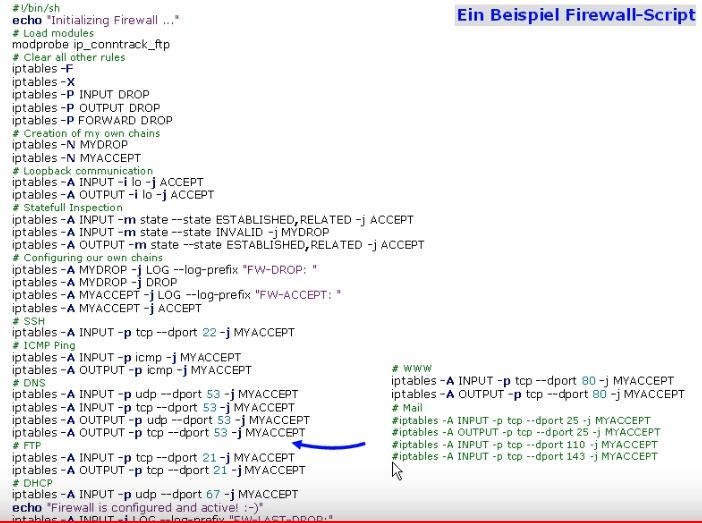
iptables -L <policy> --line-numbers # list rules with line numbers iptables -D <policy> <rule-number> iptables -F # flush rules iptables -X <policy> # eigene Policy-Chain löschen, -F löscht nur die 3 Standard Chains // default policy -> target iptables -P <policy> <target> // delete rules iptables -L <policy> --line-numbers iptables -D <policy> <rule-number> // append rule iptables -A <policy> -p <protocol> --dport <destination-port> -j DROP // Policy-chain erstellen iptables -N <chain-name>
-A - Regel anhängen -I - An bestimmter Position einfügen -i - Input interface -o - Output interface -s - Source IP -d - Destination IP -j - Action -p - Protokoll (tcp/udp/icmp/sip...) --dport - Zielport/Protokoll --sport - Quellport --sports, --dports - mehrere Ports -state, --ctstate - RELATED/ESTABLISHED
IP blocken
iptables -I INPUT -s 167.114.157.154 -j DROP
Alle eingehenden TCP ausser Port 22 verbieten
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp -m multiport ! --dports 22 -j DROP
Sonstiges
iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT # allow incoming on lo iptables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT # allow outgoing on lo iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT # allow internet traffic iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT # established and related incoming connections iptables -A OUTPUT -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # established outgoing connections
Assuming eth0 is your external network, and eth1 is your internal network, this will allow your internal to access the external
iptables -A FORWARD -i eth1 -o eth0 -j ACCEPT
Block or reject packets/traffic
iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate INVALID -j DROP # drop invalid packets iptables -A INPUT -s 15.15.15.51 -j DROP # block an ip iptables -A INPUT -s 15.15.15.51 -j REJECT # reject an ip (with answer!)
To block connections from a specific IP address, e.g. 15.15.15.51, to a specific network interface, e.g. eth0
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -s 15.15.15.51 -j DROP
Allow incoming SSH
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
Allow incoming SSH from Specific IP address or subnet
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -s 15.15.15.0/24 --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
Allow outgoing SSH
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
Allow Incoming Rsync from Specific IP Address or Subnet
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -s 15.15.15.0/24 --dport 873 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 873 -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
Allow incoming HTTP (port 80)
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
Allow incoming HTTP (Port 80) and HTTPS (Port 443)
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443 -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
Allow MySQL only from specific IP or Subnet
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -s 15.15.15.0/24 --dport 3306 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 3306 -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
If you want to delete the rule that drops invalid incoming packets (-A INPUT -m conntrack –ctstate INVALID -j DROP)
iptables -D INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate INVALID -j DROP
Delete Rule by Chain and Number
iptables -L --line-numbers # list rules Chain INPUT (policy DROP) num target prot opt source destination 1 ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED 2 ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere 3 DROP all -- anywhere anywhere ctstate INVALID 4 UDP udp -- anywhere anywhere ctstate NEW 5 TCP tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp flags:FIN,SYN,RST,ACK/SYN ctstate NEW 6 ICMP icmp -- anywhere anywhere ctstate NEW 7 REJECT udp -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-port-unreachable 8 REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere reject-with tcp-reset 9 REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-proto-unreachable 10 ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED … iptables -D INPUT 3 # delete rule nr. 3
Siehe auch NAT Masquerade